

Dispersants help prevent the buildup of sludge, varnish and other deposits. Their water separability is inferior to other synthetics, and their low viscosity indexes diminish cold-weather performance.Īn additive that keeps insoluble contaminants dispersed (colloidally suspended) in a lubricant, preventing the particles from settling and accumulating. Diesters offer excellent resistance to oxidation, varnish and carbon for a long fluid life.
Diesters mix with most glycols, polyalphaolefins (PAOs) and other fluids. High dielectric strength may indicate that a fluid is a good electrical insulator, while low dielectric strength might possibly signal that a fluid is contaminated with water.Ī category of base stocks typically used in reciprocating air compressors and vane compressors. Dielectric strength is measured as the minimum voltage at which an electric arc passing through a fluid causes fluid breakdown. The extent to which a fluid can withstand electric voltage without failing.

Particles are kept finely divided so that they can remain dispersed throughout the lubricant. The decay and loss of metal caused by a chemical reaction between the metal and another substance, such as contaminants in a lubricant.Īn additive that protects lubricated metal surfaces against chemical attack by water or other contaminants.Ī lubricant’s ability to separate from water.Īn additive which chemically neutralizes acidic contaminants in the oil before they become insoluble and fall out of the oil to form sludge. Also, the pitting and wearing away of metal or other solid surfaces caused by the collapse of air/vapor pockets in surrounding liquid. The formation of a pocket (bubble) of air or vapor in a liquid, typically resulting from the swift movement of a solid object (such as a propeller or piston) through the liquid. Many consider the type of carbon formed to be of greater significance that the quantity. These additives include oiliness agents, compounded oils, anti-wear agents and extreme-pressure agents.Ĭoked material formed after lubricating oil has been exposed to high temperatures. Made possible by the inclusion of certain additives in the lubricating oil that prevent excessive friction and scoring by forming a film whose strength is greater than that of oil alone.
VISCOSITY CHEMISTRY VOCABULARY FULL
The formation of blisters on the surface of a seal face, degrading it and increasing leak rates and friction, and increasing the potential for the seal shaft to fail.Ī form of lubrication effective in the absence of a full fluid film.
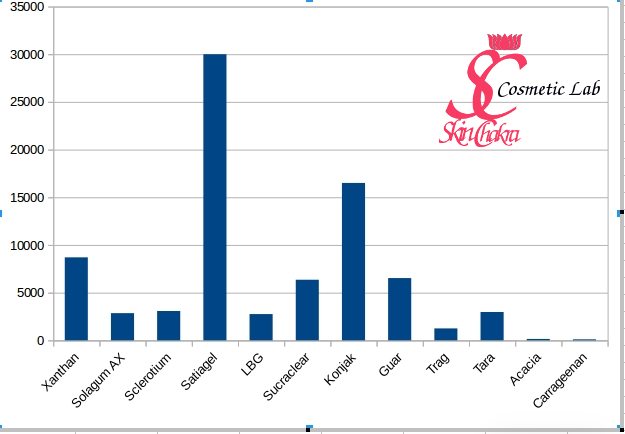
Refined petroleum oil that can be blended with other base stocks and/or supplemented with additives to make lubricants.Ĭapable of being broken down chemically, especially into innocuous products, by the action of living microorganisms in the environment. This temperature is typically several hundred degrees higher than the flash and fire point.īase stock or blend used as an inert ingredient in the manufacturing of automotive and industrial lubricants. Minimum temperature at which a combustible fluid will burst into flame without the assistance of an extraneous ignition source. Ideally, lubrication should be sufficient to prevent asperities on each metal surface from protruding through the lubricant film and making contact with other metal surfaces. Microscopic protrusion on a metal surface that typically occurs with normal finishing processes. Aromatics generally are identified by the presence of one or more benzene rings, or by exhibiting chemical behavior similar to that of benzene. Weak hydrocarbon bond that is highly reactive. It promotes the combination of small bubbles into large bubbles which burst more rapidly.Ī chemical added in small quantities to a petroleum product to increase its oxidative resistance in order to prolong its service life.Īn additive that minimizes wear caused by metal-on-metal contact by forming a film on the metal surfaces, typically activated by heat and pressure. They also have very low viscosity indexes and a tendency to swell and soften seals.Īn additive that causes foam to dissipate more rapidly. Alkylbenzene base stocks are wax-free, offer good solubility with additives and have good miscibility with certain refrigerants in the HVAC/R industry. A chemical added in small quantities to a base fluid in order to improve specific properties of the lubricant such as fluid life, lubricity, wear protection, rust protection, etc.Ī category of base stocks often used in refrigeration compressors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
